Manas Tiger Reserve
General Info Manas Tiger Reserve
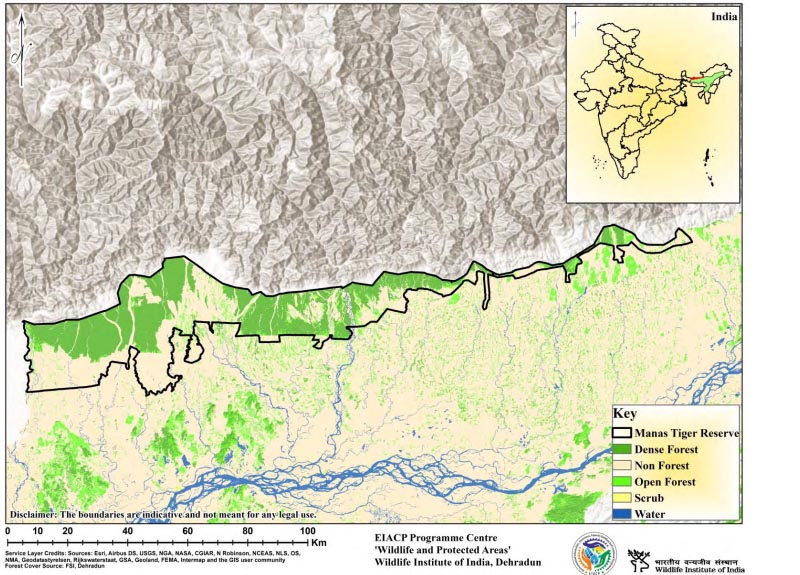
Prior to the declaration of the sanctuary, the area was Reserved Forest (R.F.) called Manas R.F. and North Kamrup R.F. The sanctuary was later extended by two successive additions in 1951 and 1955 to 391 Sq.km. by including the entire North Kamrup R.F. and the Manas R.F. Later, the Kahitama R.F., the Kokilabari R.F., and the Panbari R.F. were added, and the area was declared as Manas National Park in 1990. Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam was created in 1973 at the time of the launch of Project Tiger in India. Barnadi Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the buffer of the Reserve. There are numerous rivers crisscrossing the Reserve, namely, Sankosh, Saralbangha, Hel, Tanali, Courang, Sidli (Bhor) Aio, Manas, Beki, Pathimari, Kaladia, Tihunala, Morapagaldia, Nala, Braalia, Pbornodi, and Dhansiri. Manas is also a UNESCO Natural World Heritage Site and a part of the Ripu-Chirang Elephant Reserve. Manas Tiger Reserve is adjacent to Bhutan's Royal Manas National Park. It is located in the eastern Himalayan biodiversity hotspot. It boasts a diverse avifauna and a considerable population of certain globally threatened species, earning it the designation of an "Important Bird Area" (Rahmani et al., 2016). Manas has broadly three significant types of vegetation: a) tropical semi-evergreen, b) tropical moist deciduous, and c) alluvial grassland (Champion & Seth, 1968), along with several alluvial grass species.
Description
State : Assam
District : Baksa, Chirang, Kokrajhar and Udalguri
Coordinates :26°43′N, 90°56′E
Area : 2,837.10 Sq.km.
TR Notification year : 1973-1974
Tiger Population : 31 (All India Tiger Esitmation, 2018)