Valmiki Tiger Reserve
General Info Valmiki Tiger Reserve
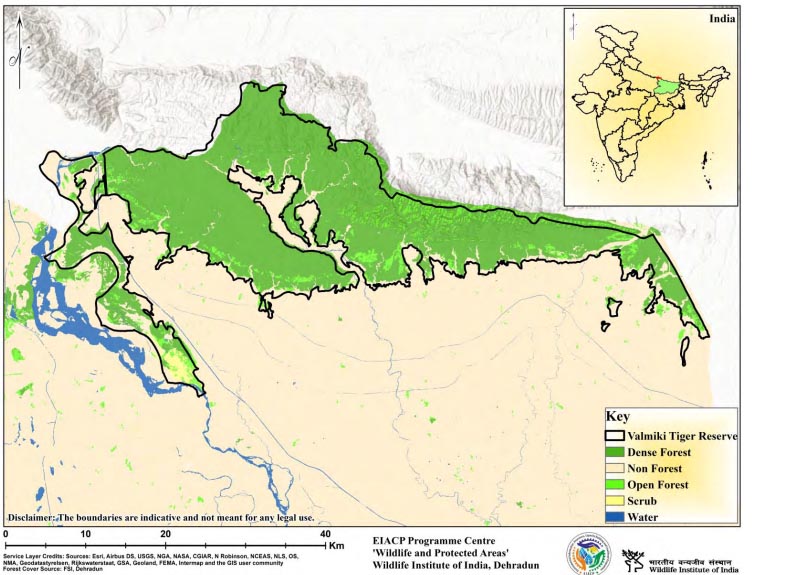
The Valmiki Tiger Reserve lies in the northernmost part of the West Champaran district of Bihar. The boundary in the north borders Royal Chitwan National park and Parsa wildlife sanctuary of Nepal. Rivers such as Gandak, Pandai, Manor, Harha, Masan, and Bhapsa flow through various reserve parts. Being part of the Siwalik Range, the Valmiki Tiger Reserve's geography comprises rolling hills and doon (valleys) drained by various rivers and streams. These rivers and streams eventually converge in the south to form flat alluvial plains. The primary water supplies for animals are these rivers and streams. Owing to the fragile nature of the parent rock material, the soil produced at the foothill is immature with loose sand.
One of the few remaining areas of terai-bhabar vegetation, Valmiki is home to a diverse array of rare and critically endangered animals, including the greater onehorned rhinoceros and tigers. Due to the Tiger Reserve's varied topographical and edaphic variables, there are seven different forest types according to Champion and Seth's classification. Moist-mixed deciduous, open-land vegetation, sub-mountainous semi-evergreen formation, freshwater swamps, riparian fringes, alluvial grasslands, high hill savannah, and wetlands are the predominant plant types.
Description
State : Bihar
District : Champaran
Coordinates : 27°10’ N, 83°50’ E
Area : 899.38 Sq.km.
TR Notification year : 1989-1990
Tiger Population : 32 (All India Tiger Esitmation, 2018)