Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
General Info Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
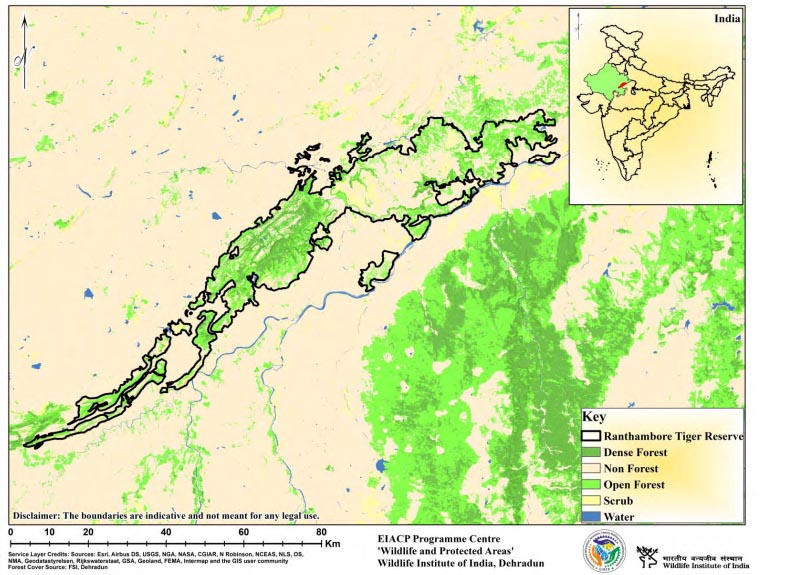
Ranthambhore is located at the confluence (great boundary fault) of the Aravalis and Vindhyan ranges and is flanked to the north by the Banas River and to the east by the Chambal River. Ranthambore Tiger Reserve consists of various sites with varying conservation histories that are almost physically isolated by only short pathways connecting them to the centre, Ranthambore National Park. Ranthambhore is part of the central Indian landscape's western block, which also contains Sariska Tiger Reserve, Kuno-Palpur Wildlife Sanctuary, Madhav National Park, Ramgarh Visdhari Wildlife Sanctuary, and Mukundara Hills Tiger Reserve. The Reserve's landscape ranges from extremely undulating (Aravalli hill range) to flat lowlands, with hills with steep slopes dominating. The Reserve's most notable archaeological features are the Ranthambore fort and medieval temples. The forest has an edaphic climax and is classified as subgroup 5Bnorthern tropical dry deciduous forests and subgroup 6B-DS1-Ziziphus shrub (Champion & Seth, 1968).
Description
State : Rajasthan
District : Sawai Madhopur, Karauli and Bundi
Coordinates : 26.0173° N, 76.5026° E
Area : 1411.29 Sq.km.
TR Notification year : 1973-1974
Tiger Population :53 (All India Tiger Esitmation, 2018)